US and UK Governments Agree To Collaborate on Nuclear, AI, and Quantum
The United States and the United Kingdom signed a memorandum of understanding on Thursday to jointly develop artificial intelligence, nuclear energy, telecommunications and quantum computing for a wide range of uses including space travel, military defense, targeted biomedical drugs and medical procedures.
The MOU, which is not legally binding and changes no existing agreements between the two countries, proposes joint research initiatives between a host of government departments and agencies in both countries to study these emerging technologies.
The two countries will form a task group to develop quantum computing hardware, software, algorithms and interoperability standards, according to the MOU.
Quantum computing has become a high-interest topic in the crypto community, as sufficiently powerful quantum computers could crack modern encryption standards that are central to crypto’s very existence.

The UK and US will also explore building 6G mobile telecommunications networks as part of the technological research and development effort.
US President Donald Trump touted the collaboration’s positive effect on investments across industrial sectors during Thursday’s press briefing with UK Prime Minister Keir Starmer. Trump said:
“This trip has galvanized $350 billion in deals across many sectors, and we are committed to ensuring that the UK is a secure and reliable supply of the best AI hardware and software on Earth, and that we supply it.”
Trump said $17 trillion was invested in the US over the last year, as the country attempts to dominate the global race to lead in artificial intelligence, digital technologies and high-performance computing systems.
Related: UK to strengthen ties with US on crypto matters: Report
Developing nuclear fusion, the next generation of nuclear energy
“The world is at the dawn of a golden nuclear age,” Thursday’s announcement from the White House said.
Both countries will collaborate on developing and deploying “advanced” nuclear energy plants, including nuclear fusion reactors, to end reliance on foreign fuels and strengthen the energy supply chain.
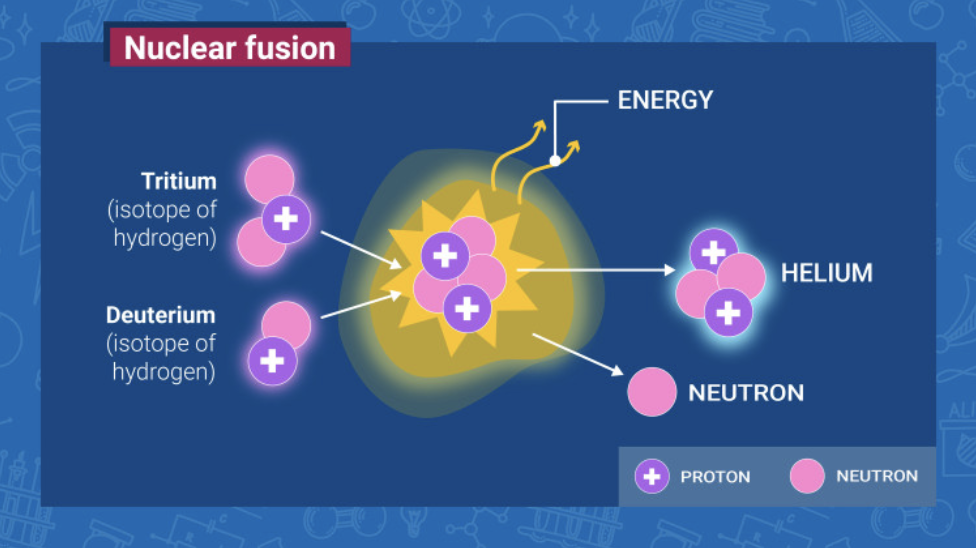
Nuclear fusion is the opposite process of nuclear fission, or the splitting of atoms, which was pioneered in the 1940s for use in atomic weapons systems.
Nuclear fusion pushes together atoms to generate energy and is much safer than nuclear fission. Nuclear fusion reactors emit significantly less radiation and do not pose the same risk of catastrophic meltdown as traditional nuclear fission reactors.
Advanced nuclear reactors can deliver a greater amount of energy, which is essential to energy-hungry artificial intelligence and high-performance computing applications.
However, abundant energy could also disrupt proof-of-work (PoW) mining algorithms used to secure certain cryptocurrencies.
If energy becomes so abundant and cheap to produce, the barrier imposed by proof-of-work may deteriorate, allowing malicious actors to attack PoW protocols through spam transactions and 51% attacks.
The next steps in the collaborative effort
The US and UK will establish an “Executive Branch-level Working Group” in the next six months and begin to collaborate on research and development in annual meetings.
However, the White House also clarified that the MOU does not “create any legally binding obligations” and neither country is obligated to spend any money on the initiatives or alter existing agreements.
Magazine: UK’s Orwellian AI murder prediction system, will AI take your job? AI Eye